| Different telephone carriers charge different rates for calls placed to different areas. Your PBX may use different telephone carriers to make calls to different areas in an effort to reduce costs. Automatic Route Selection (ARS) is a feature which automatically selects different carriers each time a CO line call is made. In order to use ARS effectively, various ARS-related tables must be preprogrammed to tell the PBX which calls should be placed using which carriers, during which time of day. If you do not activate ARS, if ARS is bypassed, or if you do not use multiple carriers, CO line calls will be connected via the carrier contracted for each line (default carrier). | |
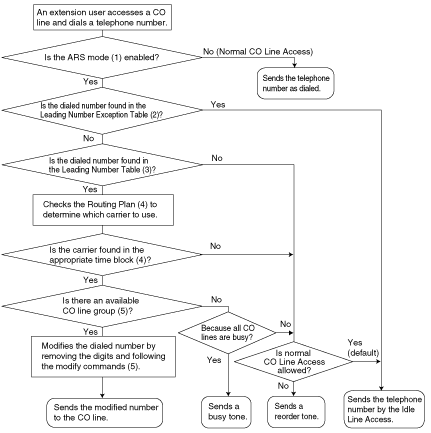
| [Carrier Selection Procedure Flowchart] The numbers in parentheses indicate the corresponding items found under [Programming Procedures] on the following pages. | |
|
| 1. | ARS Mode ( ARS is turned on by selecting under which circumstances it operates — either when an extension user makes a call using the Idle Line Access method, or when any CO Line Access method is used. ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
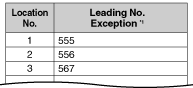
| 2. | Leading Number Exception Table Once ARS is activated, store the telephone numbers that will bypass ARS in the Leading Number Exception Table. Note that the first few digits (leading number) of a telephone number, such as an area code or local exchange, can also be stored, so that all calls to those areas or exchanges are exempted from ARS. Also note that the CO Line Access number is always ignored by ARS and does not need to be programmed here. Calls that are exempt from ARS are connected to the user-selected line, via the default carrier for that line. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
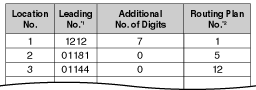
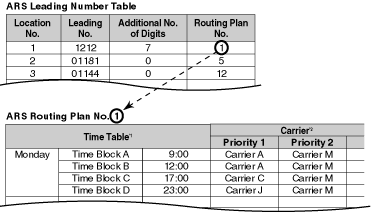
| 3. | Leading Number Table Next, store the leading numbers of telephone numbers that should be routed by ARS, and assign a Routing Plan to each leading number that will control how calls containing these leading numbers are routed. When an extension user dials a number which contains a leading number stored in the ARS Leading Number Table, the call will be routed the corresponding Routing Plan assigned here. Note that the CO Line Access number is always ignored by ARS and does not need to be programmed here. Before programming the details of each Routing Plan (explained below), you can simply assign here the same Routing Plan number to all the different leading numbers which will be routed the same way. If a dialed number matches two or more leading numbers stored in the ARS Leading Number Table, the lowest numbered location will have priority. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4. | Routing Plan Since the preferred carrier may vary depending on the time of day, you can create an ARS-specific time table and break each day of the week into different time blocks. A different carrier can then be assigned to each time block. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
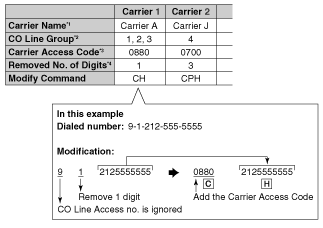
| 5. | Carrier Table Each carrier must be programmed in the Carrier Table. Here each carrier is assigned a carrier number, name, the CO lines it is used with, etc. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6. | ARS Options | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||