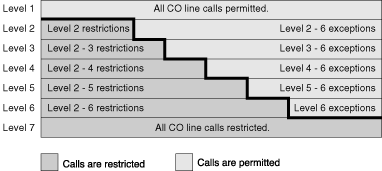
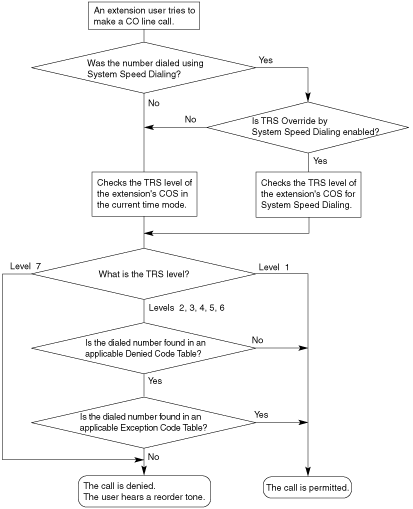
| Toll Restriction (TRS) can prohibit extension users from making certain CO line calls, based on the Class of Service (COS) assigned to them ( Each COS is assigned a TRS level for each time mode; level 1 grants the highest level of authorization, allowing all CO line calls to be made, and level 7 grants the lowest level of authorization, prohibiting all CO line calls from being made. TRS levels 2 through 6 are used to restrict calls by combining preprogrammed Denied and Exception Code Tables, explained below. Each COS can also have a separate TRS level applicable to calls made using System Speed Dialing. A TRS check is applied each time a dialed number is sent to a CO line after an extension user goes off-hook and seizes a line. |
| Denied Code Tables are preprogrammed lists containing the first few digits (leading number) of telephone numbers which may not be called. All outgoing CO line calls made by TRS level 2 through 6 users are compared to at least one Denied Code Table, and when the leading number of a dialed telephone number (not including the CO Line Access number) matches an entry found in the applicable table, the call is denied. There are five Denied Code Tables. Each table applies to a corresponding TRS level as well as the level(s) preceding it, as explained below. |
| Exception Code Tables are preprogrammed lists of leading digits or complete telephone numbers which are checked against every dialed number prohibited by a Denied Code Table. When a user dials a number prohibited by a Denied Code Table, it is compared to at least one Exception Code Table. If the dialed number matches an entry found in the applicable Exception Code Table, the call is permitted. There are five Exception Code Tables. Each table applies to a corresponding TRS level as well as the level(s) preceding it, as explained below. |
TRS Override by System Speed Dialing
| When TRS Override by System Speed Dialing is enabled for the PBX, each COS has an additional TRS level applicable only to calls made using System Speed Dialing. This allows extension users to use System Speed Dialing to make CO line calls which are normally prohibited by the TRS level of their assigned COS. If, for example, a user's TRS level is 7, that user normally cannot make any CO line calls. However, if the same user's TRS level for System Speed Dialing is level 1, the user can make a CO line call to any number stored in System Speed Dialing. |
| The Denied Code Tables and Exception Code Tables which apply to each TRS level are explained below. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
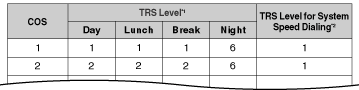
[Programming Example: TRS Level] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [Flowchart] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|