| A T1 line carries twenty-four 64 kbps-voice channels at 1.5 Mbps, and can be used as a public or private line. Voice is digitized by Pulse Code Modulation (PCM). |
| 1. | Channel Type | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | T1 Features | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Description
| A T1 line carries twenty-four 64 kbps-voice channels at 1.5 Mbps, and can be used as a public or private line. Voice is digitized by Pulse Code Modulation (PCM). |
| 1. | Channel Type | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | T1 Features | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Conditions
| • | If a T1 line is used as a public line, the channel type depends on the contract with the telephone company. |
Programming References
| • | PC Programming Manual |
| • | 2.8.33 [1-1] Slot—Port Property - T1 Port |
| • | 2.8.34 [1-1] Slot—Port Property - T1 Port—Connection Command |
| • | PT Programming Manual |
| • | None |
1.17.2 TAFAS (Trunk Answer From Any Station)
Description
| A ring tone is sent through an external pager (loudspeaker) when an incoming call is received. Any extension user can answer the call. |
Conditions
| • | Hardware Requirement: A user-supplied external pager |
| • | Floating Extension Number A floating extension number can be assigned to an external pager (default: 600). An external pager is accessed by dialing its floating extension number. |
| • | Pager Volume It is possible to change the volume level of an external pager through system programming. |
Installation Manual References
| • | 3.12 Connection of Peripherals |
Programming References
| • | PC Programming Manual |
| • | 2.9.9 [2-6-1] Numbering Plan—Main—Features— |
| • | 2.9.20 [2-11-1] Audio Gain—Paging/MOH |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | 2.12.2 [5-2] External Pager |
| • | PT Programming Manual |
| • | [700] External Pager Floating Extension Number |
Operating Manual References
| • | 1.3.64 TAFAS (Trunk Answer From Any Station) |
Description
| Tenant service is a cost-effective method of providing PBX services to different offices or companies located in the same building, while using only one PBX. |
| 1. | Tenant Configuration | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | System Management | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3. | Call Blocking | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Conditions
| • | The following features used by incoming call distribution (ICD) group are determined by the tenant number assigned to them (→ 1.9.1 ICD GROUP FEATURES): | ||||
|
Programming References
Feature Manual References
| • | 2.1 Capacity of System Resources |
Description
Conditions
| • | Be sure that the PBX clock is set to the correct time. |
| • | Only one timed reminder can be set for an extension at a time. Setting a new reminder clears the previous reminder. If both the extension user and the hotel operator set a timed reminder for the same extension, the timed reminder that was set most recently is effective. |
| • | Programmable Time The Alarm Ringing time, the number of alarm repeat times, and Interval time are programmable through system programming. |
| • | To use the voice message feature: An MSG card is required and a message must be recorded. An extension assigned as a manager can record messages. (→ 1.12.2 OGM (Outgoing Message)) A different message can be assigned for each time mode (→ 1.17.5 Time Service). |
Installation Manual References
| • | 3.7.5 MSG4 Card (KX-TDA0191) |
Programming References
| • | PC Programming Manual |
| • | 2.9.5 [2-3] Timers & Counters—DISA / Door / Reminder / U. Conf |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | 2.9.9 [2-6-1] Numbering Plan—Main—Features |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | 2.9.17 [2-8-3] Ring Tone Patterns—Call from Others— |
| • | 2.9.18 [2-9] System Options—Option 1— |
| • | 2.12.3 [5-3-1] Voice Message—DISA System—Option 2— |
| • | 2.13.2 [6-2] Hotel—Main— |
| • | PT Programming Manual |
| • | None |
Feature Manual References
| • | 1.15.3 Room Status Control |
Operating Manual References
| • | 1.3.65 Timed Reminder |
| • | 1.3.72 Wake-up Call |
Description
| Time modes are used by many PBX features to determine how they will function during different times of day. For example, incoming calls can be directed to sales staff during the day and to a Voice Processing System (VPS) at night, extension users can be prohibited from making long distance calls during lunch time, etc. |
| There are four time modes—day, lunch, break, and night. The start and end times of each time mode are programmed for each day of the week in a Time Table. Each Time Table has a number which corresponds to the tenant it serves, i.e., Tenant 1 uses Time Table 1, etc. |
| 1. | Time Service Switching Mode | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | Time Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3. | Features Using Time Service | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4. | Holiday Mode | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5. | Time Service Button | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Conditions
| • | The start times of the following time modes can be specified through PC programming as well as PT programming. | ||||||
| |||||||
| |||||||
| |||||||
| |||||||
| • | Time Service Switching Mode (Automatic/Manual) Button Any flexible button can be customized as the Time Service Switching Mode (Automatic/Manual) button. |
Programming References
| • | PC Programming Manual |
| • | 2.9.6 [2-4] Week Table |
| • | 2.9.8 [2-5] Holiday Table |
| • | 2.9.9 [2-6-1] Numbering Plan—Main—Features— |
| • | 2.9.12 [2-7-1] Class of Service—COS Settings—Extension Feature— |
| • | 2.11.5 [4-1-4] Wired Extension—Flexible Button |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | 2.11.13 [4-2-3] Portable Station—Flexible Button |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | 2.11.17 [4-3] DSS Console |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | PT Programming Manual |
| • | [101] Time Service Switching Mode |
| • | [102] Time Service Starting Time |
| • | [514] Time Service Manual Switching |
Feature Manual References
| • | 1.3.20 COS (Class of Service) |
| • | 1.6.3 Flexible Buttons |
| • | 1.17.3 Tenant Service |
| • | 1.17.6 TRS (Toll Restriction) |
| • | 2.1 Capacity of System Resources |
Operating Manual References
| • | 1.3.66 Time Service |
| • | 2.1.6 Time Service Mode Control |
Description
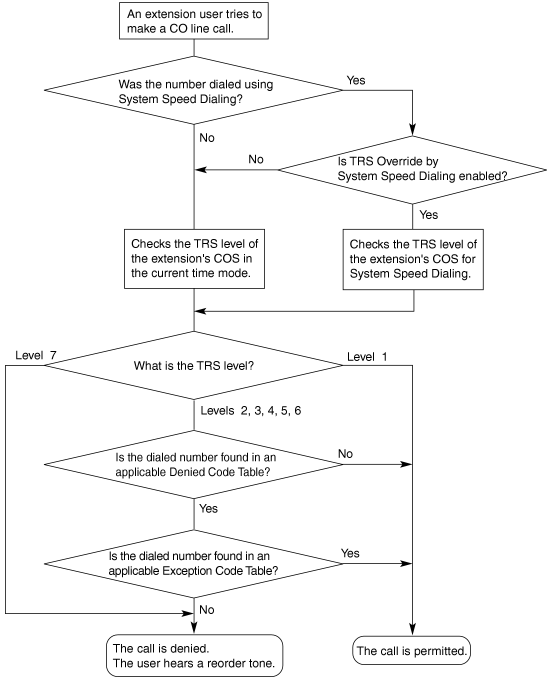
| Toll Restriction (TRS) can prohibit extension users from making certain CO line calls, based on the Class of Service (COS) assigned to them. → 2.11.1 [4-1-1] Wired Extension—Extension Settings—Main— → 2.11.10 [4-2-1] Portable Station—Extension Settings—Main— → [602] Class of Service |
| Each COS is assigned a TRS level for each time mode; level 1 grants the highest level of authorization, allowing all CO line calls to be made, and level 7 grants the lowest level of authorization, prohibiting all CO line calls from being made. TRS levels 2 through 6 are used to restrict calls by combining preprogrammed Denied and Exception Code Tables, explained below. |
| Each COS can also have a separate TRS level applicable to calls made using System Speed Dialing. |
| A TRS check is applied each time a dialed number is sent to a CO line after an extension user goes off-hook and seizes a line. |
|
| Denied Code Tables are preprogrammed lists containing the first few digits (leading number) of telephone numbers which may not be called. All outgoing CO line calls made by TRS level 2 through 6 users are compared to at least one Denied Code Table, and when the leading number of a dialed telephone number (not including the CO Line Access number) matches an entry found in the applicable table, the call is denied. |
| There are five Denied Code Tables. Each table applies to a corresponding TRS level as well as the level(s) preceding it, as explained below. |
| Exception Code Tables are preprogrammed lists of leading digits or complete telephone numbers which are checked against every dialed number prohibited by a Denied Code Table. When a user dials a number prohibited by a Denied Code Table, it is compared to at least one Exception Code Table. If the dialed number matches an entry found in the applicable Exception Code Table, the call is permitted. |
| There are five Exception Code Tables. Each table applies to a corresponding TRS level as well as the level(s) preceding it, as explained below. |
| When TRS Override by System Speed Dialing is enabled for the PBX, each COS has an additional TRS level applicable only to calls made using System Speed Dialing. → 2.9.12 [2-7-1] Class of Service—COS Settings—TRS— → [300] TRS Override by System Speed Dialing |
| This allows extension users to use System Speed Dialing to make CO line calls which are normally prohibited by the TRS level of their assigned COS. If, for example, a user's TRS level is 7, that user normally cannot make any CO line calls. However, if the same user's TRS level for System Speed Dialing is level 1, the user can make a CO line call to any number stored in System Speed Dialing. |
| The TRS level is determined by the telephone codes set in the Denied Code Tables and Exception Code Tables. As shown in the table below, the Denied Code Tables for the higher levels are applied to all levels below it, and the Exception Code Tables for the lower levels are applied to all levels above it. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [Usage Example] Using this method, certain outgoing CO line calls (e.g., international/cellular phone/long distance) can be restricted as in the example below: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In this example, a level 1 user can make any CO line calls. A level 2 user can make international calls to the countries where clients are located, and can also make cellular phone/long distance/local calls. A level 3 user cannot make international/cellular phone calls apart from to the boss's cellular phone, but can make long distance/local calls. A level 4 user cannot make any international/cellular phone/long distance calls, but can make local calls. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To set TRS as in the example above, it is necessary to program the Denied Code and Exception Code Tables as follows: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRS Settings for Each Level Through system programming, it is possible to select a different method of TRS. With this method, each level has its own separate set of denied codes and exception codes, which are only applied to that level. → 2.14.5 [7-5] Miscellaneous— |
|
Denied Code Tables*1 |
Exception Code Tables*2 | ||||
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
| [Usage Example] Using this method, it is possible to restrict certain CO line calls (e.g., international/cellular phone/long distance) on a department basis, as follows: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In this example, a level 1 user can make any CO line calls. A level 2 user can only make international calls to the country where the factory is located, and can also make cellular phone/long distance/local calls. A level 3 user can only make cellular phone calls to the company cellular phone, and can also make any international/long distance/local calls. A level 4 user cannot make any international calls or most long distance calls, but can make long distance calls to cities where clients are located, cellular phone calls and local calls. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To set TRS as in the example above, it is necessary to program the Denied Code and Exception Code Tables as follows: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Conditions
| WARNING The software contained in the TRS feature to allow user access to the network must be upgraded to recognize newly established network area codes and exchange codes as they are placed into service. |
| Failure to upgrade the on-premise PBXs or peripheral equipment to recognize the new codes as they are established will restrict the customer and the users of the PBX from gaining access to the network and to these codes. |
| KEEP THE SOFTWARE UP TO DATE WITH THE LATEST DATA. |
| • | TRS checks are performed for all calls made by: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • | The PBX can also be programmed to perform a TRS check for numbers that contain non-digits ( → 2.14.5 [7-5] Miscellaneous— |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • | TRS can also be programmed to check digits that are dialed after External Feature Access, such as when trying to transfer a call to an outside party. (→ 1.5.1 EFA (External Feature Access)) → 2.14.5 [7-5] Miscellaneous— |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • | Host PBX Access Code/Special Carrier Access Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • | ARS If ARS is applied to a dialed number, TRS will check the user-dialed number, not the modified number produced by ARS. You do not need to program ARS-modified numbers in any of the TRS Tables. Additionally, when using ARS, TRS will ignore the Host PBX Access code or Special Carrier Access code. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • | Dialing Digit Restriction during Conversation TRS can also limit the number of digits which may be dialed by an extension user while the user is engaged on a received CO line call. If the number of dialed digits exceeds the limit, the line will be disconnected. → 2.14.5 [7-5] Miscellaneous— |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • | It is possible to select through system programming whether the CO line is disconnected when the Inter-digit time expires without the TRS check being completed. → 2.14.5 [7-5] Miscellaneous— |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • | When one of the following features is used, the TRS level of the extension can be temporarily changed. If two or more of these features are used simultaneously (Dial Tone Transfer is used while the extension is locked, for example), the TRS level of the feature with the highest priority is applied for the duration of the call. The numbers below (1 through 4) indicate the priority of each feature, with 1 having the highest priority, and 4 having the lowest. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Programming References
| • | PC Programming Manual |
| • | 2.9.12 [2-7-1] Class of Service—COS Settings—TRS |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | 2.11.1 [4-1-1] Wired Extension—Extension Settings—Main— |
| • | 2.11.5 [4-1-4] Wired Extension—Flexible Button |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | 2.11.10 [4-2-1] Portable Station—Extension Settings—Main— |
| • | 2.11.13 [4-2-3] Portable Station—Flexible Button |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | 2.11.17 [4-3] DSS Console |
| • | → |
| • | → |
| • | 2.14.1 [7-1] Denied Code |
| • | 2.14.2 [7-2] Exception Code |
| • | 2.14.3 [7-3] Special Carrier |
| • | 2.14.5 [7-5] Miscellaneous |
| • | PT Programming Manual |
| • | [300] TRS Override by System Speed Dialing |
| • | [301] TRS Denied Code |
| • | [302] TRS Exception Code |
| • | [501] TRS Level |
| • | [509] TRS Level for System Speed Dialing |
| • | [602] Class of Service |
Feature Manual References
| • | 1.1.3 ARS (Automatic Route Selection) |
| • | 1.3.15 CO Line Access |
| • | 1.3.20 COS (Class of Service) |
| • | 1.16.7 Speed Dialing, System |
| • | 1.17.5 Time Service |
| • | 2.1 Capacity of System Resources |