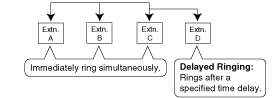
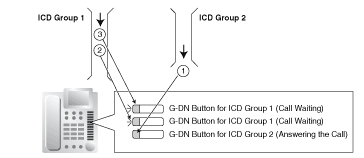
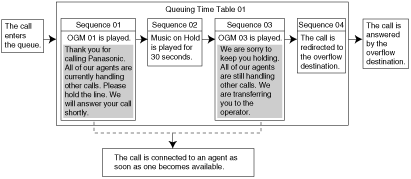
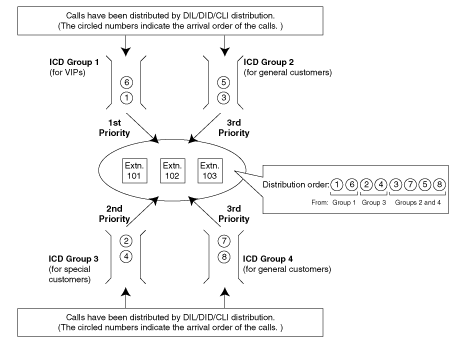
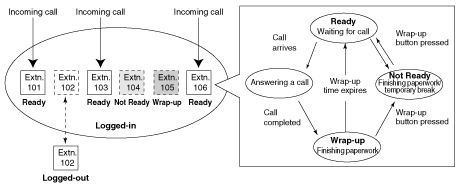
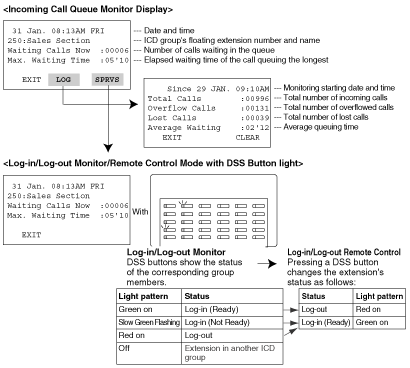
| | An outgoing message (OGM) is played for the caller. |
| | Once the message has been played, the next sequence is activated. |
|
| | The caller waits for the specified time while hearing a ringback tone or Music on Hold. |
| Music on Hold is played for the caller for the specified amount of time.
If an OGM command has not been programmed for a sequence preceding the Wait command, the caller will hear a ringback tone for the specified amount of time. |
|
| | Jumps to a specified sequence. Used to create a loop within the table. |
| |
| | Directs the call to the overflow destination. |
| |
| | |
| | Skips to the next sequence. |
| | If assigned to sequence 01, the Queuing Time Table will be disabled. |
|