1.9 I
1.9.1 ICD GROUP FEATURES
| 1. |
Group Call Distribution [→ 1.9.2 ICD Group Features—Group Call Distribution]
Incoming calls are distributed using one of the following methods: |
| |
Distribution Method |
Description |
| Uniform Call Distribution (UCD) |
|
| Calls are distributed evenly to a different extension each time a call is received. |
| |
|
| An idle extension is searched for in the specified order, always starting from the same location. |
| |
|
| All extensions in the incoming call distribution group ring simultaneously. |
|
|
|
|
| 2. |
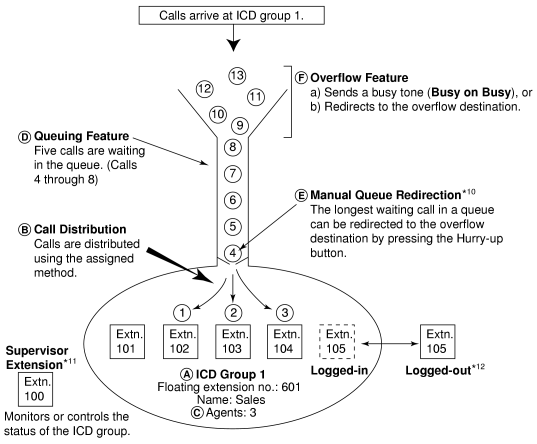
Queuing Feature [→ 1.9.6 ICD Group Features—Queuing]
If a preprogrammed numbers of extensions in an incoming call distribution group are busy, a preprogrammed number of additional calls can wait in a queue.
While calls are waiting in the queue, an outgoing message (OGM) or Music on Hold can be sent to the waiting callers.
|
| 3. |
VIP Call [→ 1.9.8 ICD Group Features—VIP Call]
It is possible to assign a priority to incoming call distribution groups so that incoming calls can be received in priority order.
|
| 4. |
Overflow Feature [→ 1.9.5 ICD Group Features—Overflow]
A call is redirected to a preprogrammed destination when it cannot be answered or queued (Intercept Routing—Overflow in an Incoming Call Distribution Group). It is also possible to send a busy tone (Busy on Busy) or disconnect the line.
|
| 5. |
Incoming Call Distribution Group Controlling Feature |
| |
Feature |
Description & Reference | |
|
Member extensions can join the group to handle calls (Log-in) or leave the group for a break (Log-out).
They can leave the group temporarily when they are away from their desks, to prevent calls being sent to their extensions. |
|
| → 1.9.3 ICD Group Features—Log-in/Log-out |
| |
|
| Incoming Call Queue Monitor |
|
|
| Log-in/Log-out Monitor and Remote Control |
|
Monitor: The supervisor extension can monitor the log-in/log-out status of the group members.
Remote Control: The supervisor extension can change the status of the members. |
|
| → 1.9.7 ICD Group Features—Supervisory |
|
|
| • |
One extension can belong to multiple incoming call distribution groups. |
| • |
ICD Group button
An Incoming Call Distribution (ICD) Group button can be assigned on a flexible button for each incoming call distribution group. It receives the incoming calls to the group.
One extension can have more than one ICD Group button of the same or different incoming call distribution groups (Multiple ICD Group). If all ICD Group buttons in the same incoming call distribution group are occupied, the next incoming call will be held in a queue or will overflow. If the ICD Group button is not assigned, incoming calls will arrive at the INTERCOM, CO or PDN button.
The mode of ICD Group buttons can be selected through system programming, as follows: |
|
| – |
Standard Mode (Group DN Button Mode)
An extension can have an ICD Group button for an incoming call distribution group that the extension does not belong to through system programming. However, the ICD Group button will not receive calls to that group. |
| – |
Enhanced Phantom Button Mode
An extension can join an ICD Group just by creating a button for that group, even if the extension was not previously registered as a member. When the button is created, the extension will be automatically registered in the lowest-numbered available member slot for the group. Calls to the group can be received at the extension with no further programming. If no member slots are available for that group, the button cannot be created and an alarm tone will be heard.
When creating an ICD Group button in this mode, the user can also specify the delayed ringing settings.
If an extension user deletes the last ICD Group button at his extension for a certain group, he will also be deregistered as a member from that group. |
|
| • |
Group FWD
The FWD feature can be assigned on an incoming call distribution group basis. |
| • |
COS for Incoming Call Distribution Groups
Each incoming call distribution group is assigned a COS number. Group FWD to an outside party can be enabled or disabled for each COS. The COS for incoming call distribution groups is also used for the Internal Call Block feature; when an extension user calls an incoming call distribution group, the PBX checks the COS of the calling extension against the COS of the incoming call distribution group (→ 1.9.14 Internal Call Block). |
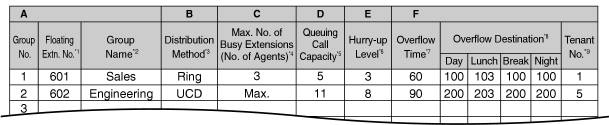
1.9.2 ICD Group Features—Group Call Distribution
Incoming calls directed to an incoming call distribution group are distributed to the member extensions using the selected distribution method until a preprogrammed number of extensions (agents) are busy with calls. When incoming calls exceed the number of available extensions, calls enter a queue (→ 1.9.6 ICD Group Features—Queuing).
|
| 1. |
Distribution Method
One of the three distribution methods below can be assigned to each incoming call distribution group. |
| |
Distribution Method |
Description |
| Uniform Call Distribution (UCD) |
|
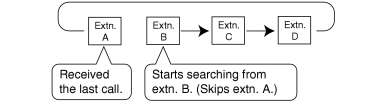
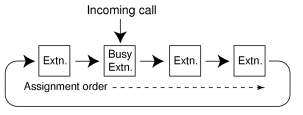
| Calls are distributed evenly to a different extension each time a call is received. Extensions are hunted in a circular way in the preprogrammed order for the group, starting at the extension after the extension that received the last call. |
|
|
|
| Depending on system programming, calls can be directed to the longest idle extension. This is known as Automatic Call Distribution (ACD). |
| |
|
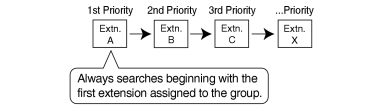
| An idle extension is searched for using the preprogrammed order for the group. |
|
|
| |
|
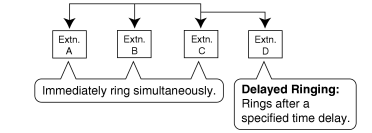
All extensions in the group ring simultaneously.
Delayed Ringing:
Delayed ringing or no ringing can be programmed for each extension in the group. The call can be answered by pressing the flashing button even if no ring or a delayed time is set. |
|
|
|
|
| 2. |
Call Waiting for Incoming Call Distribution Group (Group Call Waiting)
When there are no available extensions in an incoming call distribution group, the group members can receive the Call Waiting tone. To use this feature: |
|
| • |
Select the Group Call Waiting mode through system programming. This determines the distribution method for waiting calls. |
| • |
Member extensions must assign the Call Waiting mode individually, or they will not be notified. (→ 1.3.10 CALL WAITING FEATURES) |
|
|
| [How the Group Call Waiting Feature Activates] |
|
|
|
|
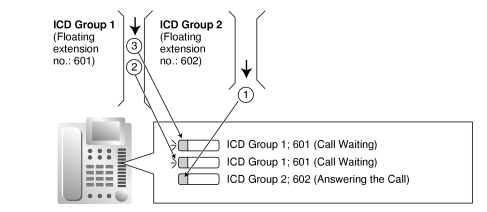
| Incoming calls enter the queue immediately. Member extensions do not receive the Call Waiting tone. |
|
|
|
[Example] |
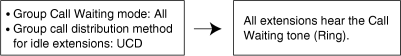
|
|
[ICD Group Button for Group Call Waiting]
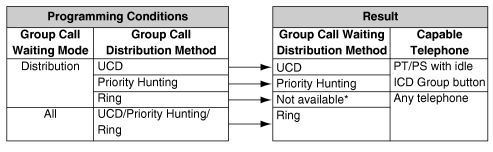
The way that the Group Call Waiting feature works depends on the Group Call Waiting Distribution method as follows: |
| a) |
Ring: The Group Call Waiting feature activates for all busy member extensions (even when the extensions do not have ICD Group buttons) simultaneously for only one incoming call—additional calls will wait in a queue. |
| b) |
UCD/Priority Hunting: The Group Call Waiting feature activates on an idle ICD Group button located on busy member extensions in a certain order. (This order depends on the type: UCD or Priority Hunting.) Calls will arrive at idle buttons until all ICD Group buttons are occupied—additional calls will wait in a queue. |
|
Note
|
In method b), if an extension has one or more ICD Group buttons for an incoming call distribution group and all the ICD Group buttons on the extension are occupied, the Group Call Waiting feature for the group will not work at the extension. |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| 3. |
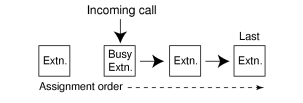
No Reply Redirection (UCD or Priority Hunting Method)
If a call received at a member extension is not answered within a preprogrammed time period (No Answer time), the call will be redirected to the next member extension. If there is no idle group member, the call queues at the target extension until a group member becomes available. |
| • |
Automatic Call Distribution (ACD)
When a KX-NCS4910 (Activation Key for Software Upgrade to Enhanced Version) is installed in the PBX, and the distribution type is set to Uniform Call Distribution, it is possible to select whether incoming calls are distributed to idle extensions evenly in order (UCD), or to the extension that has been idle the longest (ACD). |
| • |
FWD/DND Extension
System programming for each incoming call distribution group is required to skip or ring extensions which have the FWD or DND feature set. If set to ring, the FWD/DND settings are ignored. (→ 1.4.10 DND (Do Not Disturb), → 1.6.6 FWD (Call Forwarding)) |
| • |
The Group Call Waiting feature cannot be used with the VIP Call feature (→ 1.9.8 ICD Group Features—VIP Call) and/or Wrap-up feature (→ 1.9.3 ICD Group Features—Log-in/Log-out). To use the VIP Call feature and/or Wrap-up feature, Call Waiting mode on each extension should be off. |
1.9.3 ICD Group Features—Log-in/Log-out
Members of an incoming call distribution group can join (Log-in) or leave (Log-out) the group manually.
They can leave the group temporarily when they are away from their desks, to prevent calls being sent to their extensions. They can return to the group when they are ready to answer calls.
|
Wrap-up:
While logged in, a member extension can have a preprogrammed time period automatically for refusing calls after completing the previous call (Wrap-up time). While the Wrap-up timer is active, calls to all incoming call distribution groups to which the extension belongs will skip the extension so that the extension user can perform necessary tasks such as reporting on the previous call.
Wrap-up mode can also be activated manually (Not Ready) by pressing the Wrap-up button.
|
|
[Log-in/Log-out and Wrap-up Status Example] |
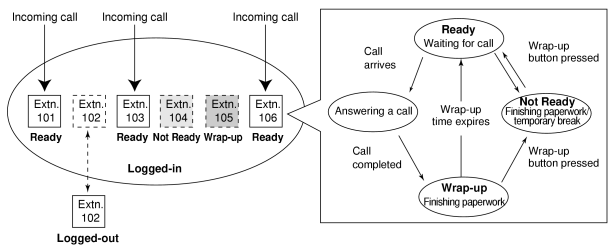
|
|
| • |
It is programmable whether the last remaining logged-in extension can log out. |
| • |
Log-in/Log-out Button
A flexible button can be customized as the Log-in/Log-out button with the following parameters: |
| |
Parameter |
Usage |
Light Pattern | |
Red on |
Off | |
|
Used with an ICD Group button, or with the floating extension number of an incoming call distribution group, or with  (All). (All). |
|
|
|
| Floating extension number of a specified incoming call distribution group |
|
| Used to log in to or out of the specified incoming call distribution group. |
|
|
|
 (All) (All) |
|
| Used to log in to or out of all incoming call distribution groups to which the extension user belongs. |
|
|
|
|
| • |
If an ICD Group button is assigned, it also shows the log-in/log-out status of the corresponding group. The light pattern is the same as the Log-in/Log-out button that includes the group number. |
| • |
Wrap-up Timer |
|
| – |
Two wrap-up timers can be programmed, an ICD Group member wrap-up timer and an extension wrap-up timer. System programming selects which timer is used. When the ICD Group member wrap-up timer is selected, the timer is only activated after calls to the extension through an ICD Group. When the extension wrap-up timer is selected, the timer is activated after all calls to or from the extension, including a retrieved call on hold. |
| – |
Only calls from ICD Groups cannot be received during the wrap-up time. Other calls are received as normal. |
| – |
The wrap-up timer does not work for SIP extensions or PS Ring Groups. |
|
| • |
Wrap-up Button
A flexible button can be customized as the Wrap-up button. It shows the current status as follows: |
| |
Light pattern |
Status | |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| Ready (Wrap-up mode cancel) |
|
|
| • |
When a PS in Wireless XDP Parallel Mode completes a call, neither the PS nor its wired telephone can have Wrap-up time. (→ 1.20.5 Wireless XDP Parallel Mode) |
| • |
Automatic Log-out
A member extension may be logged out automatically, if the Unanswered time expires a preprogrammed number of times consecutively. The number of consecutive unanswered calls can be assigned for each incoming call distribution group. If the extension is a member of more than one incoming call distribution group, the unanswered number is counted across all corresponding incoming call distribution groups. It is possible to return to log-in mode manually.
The Automatic Log-out feature does not work for extensions in an incoming call distribution group using the Ring distribution method (→ 1.9.2 ICD Group Features—Group Call Distribution). |
| • |
Log-in/Log-out Monitor
The supervisor extension can monitor and control the log-in/log-out status of the incoming call distribution group members. (→ 1.9.7 ICD Group Features—Supervisory) |
| • |
Log-in/Log-out Information on SMDR
Log-in/Log-out information can be printed out on SMDR. (→ 1.16.3 SMDR (Station Message Detail Recording)) |
1.9.4 ICD Group Features—Outside Destinations
Up to 4 outside parties or destinations at another PBX can be assigned as members of an Incoming Call Distribution (ICD) Group, using the following method: A virtual PS is registered as a member of the ICD Group. Then, the telephone number of the outside destination is specified as the FWD—All Calls destination. Calls to the ICD Group will also ring at the outside destination as if that destination were an extension within the PBX.
This is useful in situations such as the following: |
| • |
An extension user can have his PT and multiple cellular phones ring together for calls. |
| • |
An employee who is not in the office, but is still available to answer calls, can receive calls to an ICD Group. |
|
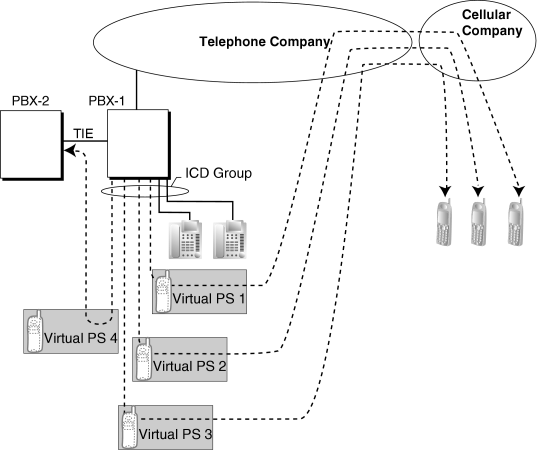
|
|
Cellular Phone XDP Parallel
|
| The extension registered first in an ICD Group can program the Forward settings for CO line calls to up to 4 virtual PSs through PT programming. Using this feature, an extension user can assign his cellular phone to ring with his PT, so that he can easily receive CO line calls even when not at his desk. |
| • |
The KX-NCS4910 (Activation Key for Software Upgrade to Enhanced Version) is required to use this feature. |
| • |
For this feature to be activated, the following conditions must be met: |
|
| – |
A virtual PS is assigned as a member of the ICD Group. (→ 1.19.2 Virtual PS) |
| – |
The forwarding type of the virtual PS is set to All Calls. (→ 1.6.6 FWD (Call Forwarding)) |
| – |
The forwarding destination is an outside party, including an extension at another PBX in the network. |
| – |
FWD to CO line is allowed through COS programming for the virtual PSs. |
| – |
The distribution method for the ICD Group is set to Ring. (→ 1.9.2 ICD Group Features—Group Call Distribution) |
|
| • |
Up to 4 virtual PSs can be assigned to a single ICD Group. If more than 4 are assigned, the 4 virtual PSs with the lowest member numbers are available. |
| • |
LCOT CO lines and channels of a T1 CO line set to LCOT do not support this feature. |
| • |
Calls to an ICD Group will ring at a virtual PS even if all of the other extensions assigned to the group are busy. |
| • |
If all members of an ICD Group are virtual PSs, and CO lines are available but the called parties are all busy, neither the queuing or overflow features will operate. Therefore, it is recommended that at least one PT or SLT is also assigned to an ICD Group. |
| • |
To log in to or out of a group, a virtual PS user can access the PBX through DISA, enter the Walking COS feature number (if required), and access log-in/log-out settings. |
| • |
Delayed ringing can be assigned for virtual PSs in the same way as for other extensions. |
| • |
The wrap-up time feature is not available for virtual PSs. |
| • |
When forwarding calls to a public CO line, system programming selects whether the CLIP number of the calling party or of the virtual PS is sent to the forward destination.
When calling using a private network, the CLIP number of the calling party will always be sent. |
1.9.5 ICD Group Features—Overflow
| When waiting calls exceed the waiting queue capacity, they may be redirected to a preprogrammed destination or a busy tone may be sent to the callers by the following features: |
| 1) |
Intercept Routing—Overflow in an Incoming Call Distribution Group |
| 2) |
Busy on Busy |
|
|
| 1. |
Intercept Routing—Overflow in an Incoming Call Distribution Group |
|
| Intercept Routing—Overflow in an Incoming Call Distribution Group works in one of following conditions: |
| a) |
There is no space in the waiting queue. |
| b) |
The Queuing Time Table is not assigned and there are no extensions logged in. |
| c) |
An Overflow command is assigned to the Queuing Time Table. |
| d) |
The Overflow time expires. |
| e) |
Manual Queue Redirection is performed.
|
|
[Available Destination]
The overflow destinations can be assigned for each incoming call distribution group and each time mode (day/lunch/break/night) (→1.17.5 Time Service). The destination can be assigned as follows, depending on the above conditions. |
|
|
|
|
|
Destination |
Availability |
| Wired Extension (PT/SLT/SIP Extension/T1-OPX) |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| Floating Extension no. for SVM |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| Analog/ISDN Remote Maintenance |
|
|
| Idle Line Access no. + Phone no. |
|
|
| Trunk Group Access no. + Trunk Group no. + Phone no. |
|
|
| Extension of Another PBX (via TIE Line, Access with PBX Code) |
|
|
| Extension of Another PBX (via TIE Line, Access without PBX Code) |
|
|
|
|
| 2. |
Busy on Busy |
|
| The Busy on Busy feature works when the destination for the Intercept Routing—Overflow in an Incoming Call Distribution Group feature is not assigned in one of the following conditions: |
| a) |
There is no space in the Waiting queue. |
| b) |
The Queuing Time Table is not assigned and there are no extensions logged-in.
|
|
[Example of a)]
There are five assistants in a shop. When the answering agent number is "2", and the queuing call number is "0":
If two of the assistants are talking on the phone, the next caller will hear a busy tone to prevent the caller from thinking that there is no one in the shop or that the shop is closed. |
|
|
[Intercept Routing—Overflow in an Incoming Call Distribution Group]
|
| • |
If the Overflow time expires, and the overflow destination is unavailable: |
|
| a) |
If the CO line call arrives through the LCOT or T1 (LCOT/GCOT) card:
(1) If the call was once in a queue and an outgoing message (OGM) was sent to it, or the call reached an incoming call distribution group by using the DISA feature (→ 1.4.8 DISA (Direct Inward System Access)): The line is disconnected.
(2) In all other cases: Redirection is ignored and the Overflow timer activates again. |
| b) |
If the call arrives through another card: Redirection is ignored and the Overflow timer activates again. |
|
| • |
If a CO line call arrives through the LCOT or T1 (LCOT/GCOT) card, a busy tone will not be sent to the caller. |
1.9.6 ICD Group Features—Queuing
When a preprogrammed number of extensions in an incoming call distribution group are busy, additional incoming calls can wait in a queue. The number of calls which can wait in the queue is programmable.
While calls are waiting in the queue, the calls are handled by the Queuing Time Table, which can be assigned for each time mode (day/lunch/break/night) (→ 1.17.5 Time Service). This PBX supports a specified number of Queuing Time Tables which each have a specified number of sequences (specific commands which are performed when a caller enters a queue). The following commands can be assigned to each sequence when making a Queuing Time Table: |
| [Command Table] |
|
Command |
Description |
Condition | |
|
| An outgoing message is sent to the caller. "xx" applies to the OGM number. |
|
| After the OGM, Music on Hold will be sent and the next event in the sequence will be activated. |
| |
|
| The caller waits for the specified time while hearing a ringback tone or Music on Hold. |
|
If an OGM has not been sent to the caller, the caller hears a ringback tone.
If an OGM has been sent to the caller, the caller hears Music on Hold. |
| |
|
| Redirects to sequence c. "c" applies to the sequence number. |
|
| |
|
| Redirects to the overflow destination. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| Redirects to the next sequence. |
|
| If assigned as sequence 01, the Queuing Time Table will not be activated. |
|
|
| |
| [Programming Example of Queuing Time Table] |
|
Queuing Time
Table No. |
Sequence*1 | |
Sequence 01 |
Sequence 02 |
Sequence 03 |
Sequence 04 |
... | |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| If a call has not reached a destination by the time the final sequence is completed, the call will be disconnected. |
|
|
|
Explanation for Queuing Time Table 01: |
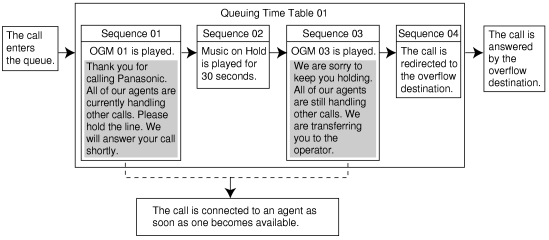
|
|
| • |
If the call is transferred to the incoming call distribution group and is handled by the Queuing Time Table:
Transfer Recall will not occur even if the Transfer Recall time expires. |
| • |
Manual Queue Redirection
It is possible to redirect the longest waiting call in a queue to the overflow destination by pressing the Hurry-up button. (If the call is already ringing at an extension, it will not be redirected.)
This feature is also known as Hurry-up Transfer. |
| • |
Hurry-up Button
A flexible button can be customized as the Hurry-up button. The number of calls queuing before Manual Queue Redirection may be performed is programmable. The button shows the current status as follows: |
| |
Light Pattern |
Calls in the Waiting Queue | |
|
| |
|
| At or under the assigned number for Hurry-up |
| |
|
| Over the assigned number for Hurry-up |
|
|
1.9.7 ICD Group Features—Supervisory
| An extension preprogrammed as a supervisor (supervisor extension) can monitor and control each member's status within the incoming call distribution group using a 6-line display PT. |
|
Feature |
Description | |
|
| The supervisor extension can monitor the status of an incoming call distribution group with the display. |
|
| Log-in/Log-out Monitor and Remote Control |
|
Monitor: The supervisor extension can monitor the log-in/log-out status of the incoming call distribution group members through the corresponding DSS button light.
Remote Control: The supervisor extension can change the status of the members by pressing the corresponding DSS button. |
|
|
|
[Example] |
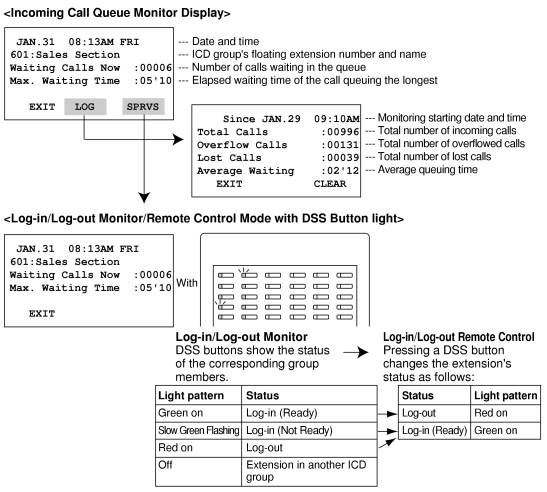
|
|
| • |
Available Extension as a Supervisor Extension |
|
| a) |
One supervisor extension can be assigned for each incoming call distribution group, but it need not belong to the group. |
| b) |
One extension can be the supervisor extension of more than one incoming call distribution group. |
|
| • |
Available Paired DSS Console
This feature is available for the KX-T7640, KX-T7440, and KX-T7441. |
| • |
Accumulation Value Clear
Accumulation value data (total incoming calls, total overflowed calls, lost calls, average queuing time) can be cleared manually. The date and time of clearing is saved and is shown on the display (monitoring starting date and time). When the value exceeds 99999 before clearing, "****" will be shown. |
| • |
If a call to an incoming call distribution group is overflowed:
If the display is in idle status, it will change to monitor mode for the corresponding incoming call distribution group automatically.
If the display is monitoring another incoming call distribution group, it will not change. |
| • |
Other Features while in Monitor Mode
The supervisor can use other features on the extension (making calls, pressing the MESSAGE button, etc.) even while in monitor mode. When each operation is finished, his telephone returns to the queue monitor display. |
1.9.8 ICD Group Features—VIP Call
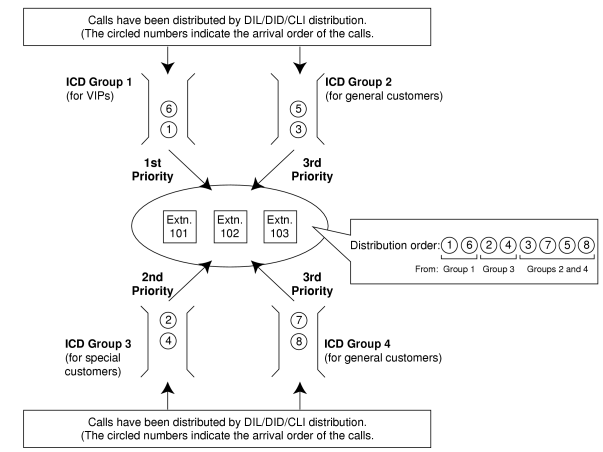
It is possible to assign a priority to incoming call distribution groups. If an extension belongs to multiple groups and the extension becomes idle, queuing calls in the groups will be distributed to the extension in priority order.
Each incoming call distribution group can enable or disable the VIP Call mode. When multiple groups enable the VIP Call mode, the incoming call distribution group with the lowest numbered group has the highest priority. When multiple groups disable the VIP Call mode, queuing calls are distributed to extensions uniformly.
[Example]
In the call center, incoming call distribution groups 1 and 3 enable the VIP Call mode, while incoming call distribution groups 2 and 4 disable the VIP Call mode. |
1.9.9 Idle Extension Hunting
| If a called extension is busy or in DND mode, Idle Extension Hunting redirects the incoming call to an idle member of the same idle extension hunting group, which can be programmed through system programming. Idle extensions are automatically searched according to a preprogrammed hunting type. |
| This feature is also known as Station Hunting. |
|
Type |
Description |
|
|
| An idle extension is searched for in the order specified in the idle extension hunting group in a circular way. |
|
|
|
| An idle extension is searched for in the order specified in the idle extension hunting group until reaching the last assigned extension. |
|
| • |
Idle Extension Hunting applies to:
Intercom, CO line, and doorphone calls to a single destination. |
| • |
An extension user can belong to only one idle extension hunting group. |
| • |
If all the searched extensions are busy:
The PBX redirects the call to an overflow destination which can be assigned for each idle extension hunting group and each time mode (day/lunch/break/night) (→ 1.17.5 Time Service).
[Available Destination] |
| |
Destination |
Availability |
| Wired Extension (PT/SLT/SIP Extension/T1-OPX) |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| Floating Extension no. for SVM |
| | |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| Analog/ISDN Remote Maintenance |
|
|
| Idle Line Access no. + Phone no. |
|
|
Trunk Group Access no. + Trunk Group no. +
Phone no. |
|
|
| Extension of Another PBX (via TIE Line, Access with PBX Code) |
|
|
| Extension of Another PBX (via TIE Line, Access without PBX Code) |
|
|
|
| • |
FWD/DND Mode
While searching for an idle extension within an idle extension hunting group, any extension that has set FWD—All Calls or DND feature will be skipped, and the call will go to the next extension in the group. |
1.9.10 INCOMING CALL FEATURES
| Each CO line functions as either a public line or a private line. Private lines are used to connect different PBXs and form a private network (→ 1.13.15 PRIVATE NETWORK FEATURES), while public lines connect a PBX to a public network, i.e., the telephone company. Certain PBX features are available depending on the networking type (public or private) of each CO line. |
| 1. |
Networking Type Used by Each CO Line |
|
|
| 2. |
Distribution Method |
|
| Each public CO line port (channel) can use a different method of directing calls to their destinations as they are received. |
|
Distribution Method |
Description |
Details in | |
|
| Directs a call to a preprogrammed destination, such as an operator, based on the CO line carrying the call. |
|
|
| Direct Inward Dialing (DID) |
|
| Directs a call received on a DID line to a preprogrammed destination based on the telephone number dialed by the caller. |
|
|
|
|
|
| Calling Line Identification (CLI) distribution is the most customizable call distribution method available. It allows calls from specific people to be directed to specific destinations, based on the callers' telephone numbers. CLI distribution, when enabled for the current time mode, takes precedence over DIL or DID distribution. |
|
Feature |
Description |
Details in |
| Calling Line Identification (CLI) Distribution |
|
| Directs a call to its preprogrammed destination if the caller's telephone number and its CLI destination has been stored in the System Speed Dialing Table. |
|
|
|
|
|
| 3. |
Available Distribution Method for Public CO Lines |
|
|
Card Type |
Port/Channel Type |
Distribution Method | |
DIL |
DID | |
|
|
| | |
|
|
| | |
|
| | |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
 : Enable : Enable |
 : Available : Available
|
|
|
|
| 4. |
Available Destination |
|
| The following destination types can be programmed as DIL, DID, or CLI destinations. |
|
Destination Type |
Availability |
| Wired Extension (PT/SLT/SIP Extension/T1-OPX) |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| Floating Extension no. for SVM |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| Analog/ISDN Remote Maintenance |
|
|
| Idle Line Access no. + Phone no. |
|
|
| Trunk Group Access no. + Trunk Group no. + Phone no. |
|
|
| Extension of Another PBX (via TIE Line, Access with PBX Code) |
|
|
| Extension of Another PBX (via TIE Line, Access without PBX Code) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 5. |
Intercept Routing |
|
| After a call has been directed to its DIL, DID, or CLI destination, the following Intercept Routing features, if programmed, can redirect the call. |
|
Type |
Description |
Details in | |
|
| If a called party does not answer a call within a preprogrammed time period (Intercept time), the call is redirected to a preprogrammed destination. |
|
| |
|
| If a called party is already handling another call, the new call is redirected to a preprogrammed destination. |
| |
|
| If a called party is in Do Not Disturb (DND) mode, the call is redirected to a preprogrammed destination. |
| |
|
| If a destination is not assigned, the call is redirected to an operator. |
|
|
|
|
1.9.11 Intercept Routing
| Redirects an incoming CO line call or intercom call to a preprogrammed destination when the original destination does not, or can not, answer the call. There are four types of Intercept Routing, described below. |
|
Type |
Description | |
|
| |
|
| If a called party is already handling a call, new calls are handled as follows: |
| – |
The call is redirected to the preprogrammed Intercept Routing—Busy destination. |
| – |
If an Intercept Routing—Busy destination is not enabled, the caller will hear a busy tone. However, if the call is made through an LCOT or T1 [LCOT/GCOT] card, the caller hears a ringback tone. |
|
| |
|
| If a called party is in Do Not Disturb (DND) mode, the call is redirected to a preprogrammed intercept destination. |
| |
|
|
|
| Intercept Routing redirects calls to destinations based on the original destination of the call, as shown in the table below. Different intercept destinations can be programmed for each time mode. Note that calls redirected by Intercept Routing—No Answer/DND are directed to the same destination, while Intercept Routing—Busy is directed to a separate destination, and the intercept destination for Intercept Routing—No Destination is always an operator. |
|
When the original destination is: |
The Available Intercept Destination is: |
| • |
Wired Extension (PT/SLT/SIP Extension/T1-OPX) |
| • |
PS |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| The destination assigned to the first extension of the VM group. |
| |
|
| If all DISA ports are busy when a call is made using DISA, one of the following can be selected through system programming: |
| • |
Disable: Busy tone is sent to the caller. When using an analog CO line, a ringback tone is sent. |
| • |
Operator: The call will be redirected to the operator. |
| • |
AA-0, AA-9: The call will be redirected to the destination assigned to that AA number. |
|
| • |
PS Ring Group** |
| • |
External Pager (TAFAS)** |
| • |
Analog/ISDN Remote Maintenance |
| • |
Other PBX Extension (TIE with no PBX Code) |
|
| Not assignable (Intercept Routing is not available.) |
|
|
|
|
| Intercept Routing for DISA will redirect a call only if all of the Direct Inward System Access (DISA) ports are busy. If Intercept Routing is activated after a call from DISA reaches the destination extension, the Intercept Routing settings assigned to that extension will be applied. |
|
|
|
|
By assigning the forward destination of a Virtual PS to a PS Ring Group or external pager, and assigning Intercept Routing destinations to the Virtual PS, calls to these destinations will be redirected to the Intercept Routing destination of the Virtual PS.
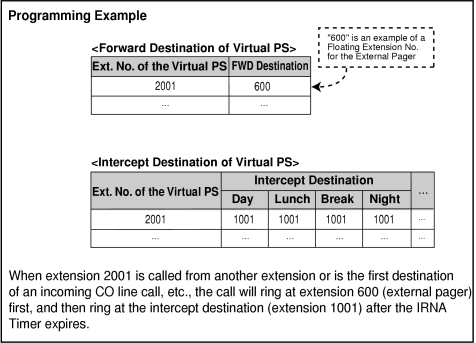 |
|
|
| [Available Intercept Destination] |
| The following can be used as intercept destinations: |
|
Intercept Destination |
Availability |
| Wired Extension (PT/SLT/SIP Extension/T1-OPX) |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| Floating Extension no. for SVM |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| Analog/ISDN Remote Maintenance |
|
|
| Idle Line Access no. + Phone no. |
|
|
| Trunk Group Access no. + Trunk Group no. + Phone no. |
|
|
| Extension of Another PBX (via TIE Line, Access with PBX Code) |
|
|
| Extension of Another PBX (via TIE Line, Access without PBX Code) |
|
|
|
| • |
If the intercept destination is busy or in DND mode and therefore cannot receive the call: |
|
| a) |
When the call was intercepted via Intercept Routing—No Answer, the call is sent back to the original destination and continues to ring at the original destination until answered. |
| b) |
When the call was intercepted via Intercept Routing—Busy and arrived through an LCOT or T1 (LCOT/GCOT) card, the call waits at the original destination. If the extension has Call Waiting activated, the user will hear a call waiting tone. When the call arrived on any other card, the caller hears a busy tone. |
| c) |
When the call was intercepted via Intercept Routing—DND and arrived through an LCOT or T1 (LCOT/GCOT) card, the call waits at the original destination and it rings. When the call arrived through any other card, the caller hears a busy tone. |
|
| • |
If the intercept destination can, but does not, answer the call:
The call continues to ring at the intercept destination until answered. |
| • |
Intercept Routing—DND on/off
Intercept Routing—DND can each be enabled or disabled for the entire system, through system programming. If enabled, calls will be routed to the appropriate destination.
If disabled, a call to an extension which is in DND mode will be handled as described below, depending on the type of line carrying the call. |
|
|
|
| a) |
LCOT or T1 (LCOT/GCOT) Card: The caller will hear a ringback tone. If in DND mode, the extension will ring. |
| b) |
All other lines: An outside caller will hear a busy tone and an extension caller will hear a DND tone. |
|
| • |
Idle Extension Hunting
If an extension is a member of an idle extension hunting group, calls to that extension will not be redirected by Intercept Routing—Busy/DND. If the extension is busy or in DND mode, calls to that extension will be redirected to the next extension in the idle extension hunting group. |
| • |
Intercept Routing for intercom calls can be enabled or disabled on a system basis.
→ 2.17.6 [10-4] Miscellaneous— Intercept—Intercept Routing for Extension Call Intercept—Intercept Routing for Extension Call |
| • |
IRNA Timer
The IRNA timer can be set on a system basis and an extension basis for each time mode (day, lunch, break, night).
→ 2.11.1 [4-1-1] Wired Extension—Extension Settings—Intercept No Answer Time— Intercept No Answer Time—Day, Lunch, Break, Night Intercept No Answer Time—Day, Lunch, Break, Night |
| • |
The Intercept Routing destination for each time mode will not apply for Intercept Routing—Busy. When the original destination is busy, the call is redirected to the Intercept Routing—Busy destination assigned through system programming. If no destination is assigned the caller will hear a busy tone. |
| • |
The time modes that are selected for CO line calls arriving at extensions and VM groups are decided on a tenant basis. |
1.9.12 Intercept Routing—No Destination
| Directs a CO line call to an operator when the call has no assigned destination. |
| • |
Intercept Routing—No Destination on/off
Intercept Routing—No Destination can be enabled or disabled for the entire system, through system programming. If disabled, the caller will hear a reorder tone.
Note that calls received through an LCOT or T1 (LCOT/GCOT) card will always be directed to an operator, even when this feature is disabled. |
| • |
If an operator is not assigned:
The default intercept destination will be the extension connected to the lowest numbered port, on the card installed in the lowest numbered slot. |
| • |
Intercept Routing—No Destination also applies to calls from doorphones. |
1.9.13 Intercom Call
| An extension user can call another extension user. |
| • |
Extension Number/Name Assignment
Extension numbers and names are assigned to all extensions. The assigned number and name of the other extension are shown on display PTs during intercom calls. |
| • |
DSS Button
It is possible to call another extension by simply pressing the corresponding Direct Station Selection (DSS) button. Any flexible button can be customized as a DSS button. |
| • |
Call Directory—Extension Dialing
Display proprietary telephone (PT) users can make a call by selecting stored names on the display. |
| • |
Alternate Receiving—Ring/Voice
A PT user can select to receive intercom calls by ring tone or by voice, through personal programming (Alternate Receiving—Ring/Voice). If a user selects voice-calling, the calling party talks to the user immediately after a confirmation tone. Denying voice-calling can also be selected. |
| • |
Alternate Calling—Ring/Voice
A caller can change the called party's preset call receiving method (ring tone or voice) temporarily. By doing so, ring-calling is switched to voice-calling, or vice versa, at the called party. The called party may deny voice-calling. |
| • |
PDN/SDN
It is not possible to temporarily change the called party's preset call receiving method when making a call using a Primary Directory Number (PDN) button or Secondary Directory Number (SDN) button (→ 1.13.7 PDN (Primary Directory Number)/SDN (Secondary Directory Number) Extension). |
| • |
Tone after Dialing
After dialing an extension number, a user will hear one of the following: |
| |
Type |
Description | |
|
| Indicates the called party is being called. |
| |
|
| Indicates the called party has set voice-calling. |
| |
|
| Indicates the called party is busy. |
| |
|
| Indicates the called party has set DND. |
|
|
1.9.14 Internal Call Block
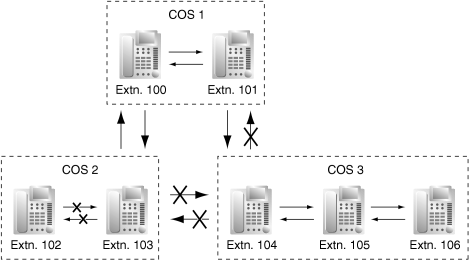
| Internal calls can be restricted based on the Class of Service (COS) assigned to the caller and to the called party. |
|
|
[Programming Example: Internal Call Block] |
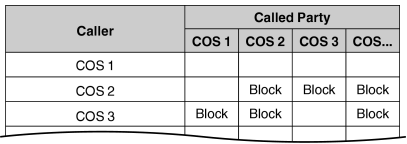
|
|
| In this example: |
| a) |
COS 1 can make calls to all extensions. |
| b) |
COS 2 can make calls to COS 1 only. (COS 2 cannot make calls to COS 2.) |
| c) |
COS 3 can make calls to COS 3 only. |
|
|
|
| • |
Internal Call Block also prohibits certain features, such as Walking Extension and Walking COS, from being performed between certain extensions. |
| • |
Any extension can make an Operator Call regardless of the Internal Call Block setting of its COS. (→ 1.12.5 Operator Features) |
| • |
Because each doorphone port is assigned a COS, the Internal Call Block feature can restrict certain extensions from calling certain doorphones. (→ 1.4.12 Doorphone Call) |
1.9.15 IP-PT (IP Proprietary Telephone)
This PBX supports the connection of IP proprietary telephones (IP-PTs), which function almost identically to normal PTs. However, they connect to the PBX over a Local Area Network (LAN), and send and receive calls using Internet Protocol (IP).
IP-PTs have two Ethernet ports for connection, primary and secondary. They are connected to the PBX through a network hub or other splitting device, and can have a PC connected to the secondary Ethernet port. |
|
[Connection Example] |
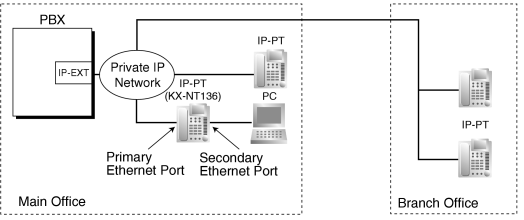
|
|
| • |
A V-IPEXT card or IP-EXT card is required to use IP-PTs. |
| • |
IP-PT registration is required through system programming before an IP-PT can be used with the PBX. An IP-PT cannot be used unless an extension number is assigned. For details on how to register IP-PTs, see the IP Networking Guide. |
| • |
The following features cannot be used with an IP-PT: |
|
|
| • |
The KX-NT265 does not have a secondary Ethernet port. |
| • |
The following optional devices are available for the KX-NT300 series IP-PT: |
|
| – |
KX-NT307(PSLP1528) Bluetooth Module |
| – |
KX-NT303 Add-on 12 Key Module (not available for KX-NT366) |
| – |
KX-NT305 Add-on 60 Key Module (not available for KX-NT366) |
|
| • |
KX-NT307(PSLP1528) Bluetooth Module
A Bluetooth wireless headset can be registered to an KX-NT300 series IP-PT containing the KX-NT307(PSLP1528) Bluetooth Module through personal programming. When Headset Mode is off, the Bluetooth headset can be used to answer calls or redial. In this case, Headset Mode will turn on automatically, and will turn off after you hang up. |
| • |
Calls made using a Bluetooth wireless headset will not be disconnected immediately when the user wanders out of range. However, if the Bluetooth wireless headset user remains out of range for a specified time period, the call will be disconnected. |
| • |
IP-PTs can be connected to the V-IPEXT/IP-EXT card as follows: |
| | |
V-IPEXT Card |
IP-EXT Card | |
| |
| |
| |
|
| KX-NT265 (version 2.00 or later) |
|
|
|
| KX-NT300 series (except KX-NT366/KX-NT305) |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
1.9.16 ISDN (INTEGRATED SERVICES DIGITAL NETWORK) FEATURES
| Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a digital switching and transmission network. ISDN transmits voice, data, and image in digital format. ISDN lines can be connected to public lines (CO lines), private lines (QSIG). |
| 1. |
ISDN Interface and Configuration |
| |
Interface Type |
Description |
Port Mode |
| Primary Rate Interface (PRI) |
|
| Provides twenty-three 64 kbps B channels for communication and one 64 kbps D channel for signaling (23B + D). |
|
| CO Line, QSIG—Master, QSIG—Slave* |
|
|
|
|
| 2. |
ISDN Supplementary Services for Public Network |
| |
Service |
Description |
Details in |
| Direct Inward Dialing (DID) |
|
| Directs a call with a DID number to the preprogrammed destination. |
|
|
| Calling Line Identification Presentation (CLIP) |
|
| Sends the caller's telephone number to the network when making a call. The called party can see the number on his or her telephone display before answering the call. |
|
|
| Connected Line Identification Presentation (COLP) |
|
| Sends the telephone number of the answered party to the network when answering a call. The caller can see the number on his telephone display when the line is connected. |
|
| Calling Line Identification Restriction (CLIR) |
|
| Prevents the caller's CLI from being presented to the called party. |
|
| Connected Line Identification Restriction (COLR) |
|
| Prevents COLP from being sent by the answered party. |
| |
|
| The PBX receives Caller ID information, such as the caller's name and telephone number, when a call is sent from the network. A display proprietary telephone (PT) user can see this information before answering the call. |
|
|
|
| 3. |
Private Networking Connection (QSIG) |
|
| Private networking with QSIG is possible using an ISDN line. Each ISDN port must be programmed so that each ISDN line has a "master" connection and a "slave" connection. |
|
|